 |
Due to its high specific surface area, stability, corrosion resistance, and photocatalytic properties, nano titanium dioxide (nTiO2) is mass produced and widely used. (The widespread use of nTiO2 inevitably leads to human exposure and environmental leakage, which in turn poses a threat to human health, animals, and the entire ecosystem. In recent years, articles published in the relevant fields of nTiO2 have grown rapidly, which also indicates that the safety of nTiO2 is being compromised. More and more attention has been paid, although existing studies have shown that (nTiO2 can absorb metals and organic pollutants through chemical binding such as electrostatic forces and chemical bonds, thereby increasing its bioavailability. However, nTiO2 is used as a carrier to promote There is a lack of systematic research on how pollutants are distributed and how they are potentially toxic after they enter the organism.
The Urban Water Environment and Water Ecology Research Group (Yan Changzhou team) of the Institute of Urban Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences has applied nTiO2 as a research object since 2013 to systematically study its accumulation and distribution of pentavalent arsenic (As(V)) in large earthworms. The effects of toxic effects showed that (nTiO2 as an effective carrier significantly increased the accumulation of As(V) in large carcasses.(With increasing nTiO2 concentration from 2 mg-Ti/L to 20 mg-Ti/L. The cumulative amount of As(V) is 2.3 and 9.8 times the arsenic accumulation in the free state, respectively.The researchers found that the distribution of nTiO2 and As(V) in the large-scale larvae was significant by combining laser ablation with plasma mass spectrometry. Correlation (2.0 mg-Ti/L (nTiO2, R=0.676, P<0.01; 20.0 mg-Ti/L nano-TiO2, R=0.776, P<0.01). This also confirms the (nTiO2 carrier effect) In addition, the study found a very interesting phenomenon that the toxic effect of As (V) on large cockroaches was not consistent with its accumulation in large cockroaches. This study attempted to explain it from the perspective of subcellular distribution. Compared with the group, (As the concentration of nTiO2 increases, the increased As(V) is mainly distributed in gold. In the detoxification phase, while increasing (nTiO2 is mainly distributed in the metal-sensitive phase. As(V) and (The difference in the subcellular distribution of nTiO2 in large larvae indicates that the partial adsorption on As(V) on nTiO2 may be in large scales. In vivo (dissociated from nTiO2. Therefore, higher concentrations of (nTiO2 (20.0 mg-Ti/L) increased As(V) toxicity, while lower concentrations (nTiO2 (2.0 mg-Ti/L) decreased. The As(V) toxicity was due to the fact that the As(V) content in the metal sensitive phase remained essentially unchanged compared to the control; on the other hand, part of the As(V) was still adsorbed on the nTiO2.
The research results were published in the international journal Environmental Science and Technology (Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.6b01215). The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41271484, 41401552, 41301346).
Germanium Plano-Convex (PCX) Lenses feature precision diamond turned surfaces making them ideal for a variety of infrared applications, including thermal imaging, infrared spectroscopy, and remote sensing. Germanium (Ge) is popular for its high index of refraction, broad transmission range, and rugged mechanical properties. These lenses are available in 25 and 50mm diameters, uncoated, or with multiple broadband coating options.
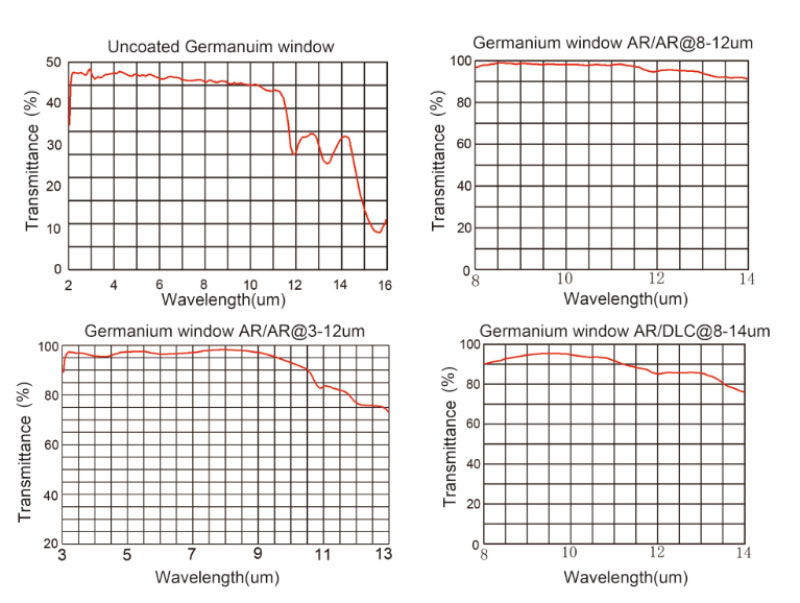
Germanium (Ge) material feature high index of refraction (around 4.0 from 2 - 14μm), an anti-reflection coating is recommended on these germanium windows for sufficient transmission in the region of interest. Germanium is subject to thermal runaway, meaning that the transmission decreases as temperature increases. As such, these germanium windows should be used at temperatures below 100°C. Germanium`s high density (5.33 g/cm3) should be considered when designing for weight-sensitive systems. 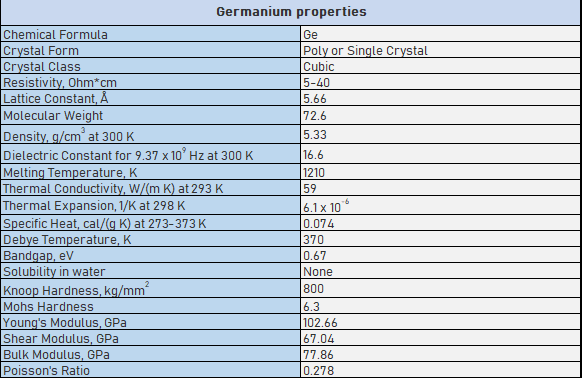
|
Germanium windows specifications |
||
| Standard precision | High-precision | |
| Dimension Tolerance | φ5-250mm+0/-0.2 | φ3-350mm+0/-0.2 |
| Thickness Tolerance | 1-50mm+/-0.1 | 1-50mm |
| Parallelism | 1 arc minute | 10 arc seconds |
| Surface Quality | 60/40 | 20/10 |
| Flatness | N<λ/2@633nm(at 50mm) | N<λ/10@633nm(at 50mm) |
| Clear Aperture | >90% | >95% |
| Chamfer | Protected <0.5mmx45deg | Protected <0.5mmx45deg |
Germanium Lens,Ge Infrared Aspheric Lens,Germanium Aspheric Lens,Germanium Infrared Lens
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.realpoooptics.com